
In the digital age, the significance of safeguarding personal information cannot be overstated. As technology continues to permeate every aspect of our lives, the need for a robust framework that respects and protects individual confidentiality becomes increasingly crucial. This section delves into strategies and practices that aim to elevate the awareness and implementation of measures to ensure that personal data remains secure and under the control of its rightful owners.
The journey towards a more guarded digital environment involves not only technological advancements but also a shift in societal norms and individual behaviors. It requires a collective effort from users, developers, and policymakers to create and maintain an ecosystem where data protection is not an afterthought but a fundamental principle. By exploring various tools and educational approaches, we can empower citizens to take proactive steps in managing their digital footprints.
This article will outline key methodologies and advocate for a culture that values personal data integrity. Through a combination of legislative support, technological innovation, and public awareness campaigns, we can move towards a future where digital secrecy is not just an option, but a standard expectation for all internet users.
Understanding the Landscape of Data Protection
In this section, we delve into the complex terrain of personal data security, exploring the multifaceted aspects that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of this critical issue. The focus is on unraveling the intricate web of factors that influence how our information is collected, used, and protected in the digital age.
The Current State of Data Protection
Today, the landscape of data protection is characterized by a dynamic interplay of technology, law, and societal norms. With the exponential growth in digital data, the stakes have never been higher for ensuring that personal information remains secure and private. This involves not only understanding the technical mechanisms that safeguard data but also the legal frameworks and cultural attitudes that shape these protections.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Technological advancements have both facilitated and complicated the task of data protection. On one hand, innovations such as encryption and secure authentication methods have bolstered the defenses against unauthorized access. On the other hand, the proliferation of data-driven technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) has expanded the potential attack surfaces, requiring more sophisticated and vigilant security measures.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Globally, various legal and regulatory frameworks aim to govern the handling of personal data. These range from the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe to various national laws that dictate how companies must treat user information. Understanding these laws is crucial for both individuals seeking to protect their data and organizations striving to comply with legal requirements.
Cultural and Societal Perspectives
Beyond technology and law, cultural attitudes towards data privacy play a significant role in shaping the landscape. Different societies have varying levels of comfort with data sharing and privacy, influenced by factors such as trust in institutions and historical precedents. These cultural nuances can significantly impact how data protection is perceived and implemented.
In conclusion, comprehending the landscape of data protection requires a multifaceted approach that considers technological, legal, and societal dimensions. By gaining a deeper understanding of these elements, we can better equip ourselves to navigate the challenges of maintaining privacy in an increasingly interconnected world.
Understanding the Landscape of Online Privacy
This section delves into the intricate world of digital monitoring, exploring how advancements in technology have reshaped the way personal data is collected and analyzed. The focus here is on comprehending the mechanisms and implications of these surveillance practices.
Digital surveillance has evolved significantly over the years, moving from simple tracking of web activities to sophisticated data mining techniques. Here are some key developments:
- Advancements in data analytics have enabled more precise and invasive forms of monitoring.
- The rise of social media platforms has led to an increase in voluntary sharing of personal information, which is then leveraged by surveillance systems.
- Government agencies and private corporations alike have expanded their capabilities to monitor online activities, often under the guise of security and marketing, respectively.
Understanding these evolutions is crucial for recognizing the extent and methods of surveillance currently in place. It also helps in identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with these practices.
Moreover, the ethical and legal implications of digital surveillance are vast. Issues such as consent, data protection, and privacy rights are central to discussions on this topic. Here are some considerations:
- The balance between security and privacy is a delicate one, often leading to debates on where to draw the line.
- The effectiveness of current laws and regulations in curbing invasive surveillance practices is under constant scrutiny.
- Public awareness and education play a significant role in shaping the public’s understanding and response to digital surveillance.
In conclusion, the evolution of digital surveillance is a complex and multifaceted issue that affects every individual who uses digital platforms. It is imperative to continue exploring and understanding these developments to better protect personal data and uphold privacy rights in the digital age.
The Evolution of Digital Surveillance
This section delves into the historical progression and current state of monitoring activities in the digital realm. It explores how surveillance practices have transformed over time, influenced by technological advancements and societal shifts.
Early Beginnings: Initially, digital surveillance was primarily focused on ensuring network security and preventing unauthorized access. However, as technology evolved, so did the scope and sophistication of these monitoring techniques.
The Rise of Big Data: With the advent of the internet and the proliferation of digital devices, vast amounts of data became available. This led to a significant expansion in the capabilities of surveillance, enabling entities to collect, analyze, and utilize data on an unprecedented scale.
Governmental Involvement: Governments around the world began to recognize the potential of digital surveillance for national security and law enforcement purposes. This led to the implementation of various programs aimed at monitoring communications and activities online, often sparking debates about the balance between security and personal freedom.
Technological Advancements: The development of advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence has further enhanced the efficiency and effectiveness of digital surveillance. These technologies can now analyze patterns and behaviors in real-time, providing deeper insights and more actionable data.
Public Awareness and Backlash: As the extent of digital surveillance became more apparent, public awareness and concern grew. This has led to increased scrutiny of surveillance practices and calls for more stringent regulations to protect individual rights and privacy.
In conclusion, the evolution of digital surveillance is a complex interplay of technological innovation, societal needs, and ethical considerations. Understanding this evolution is crucial for shaping future policies and practices that respect individual privacy while maintaining necessary security measures.
Key Privacy Laws and Their Impact
This section delves into the pivotal role of legal frameworks in shaping the protection of personal data. Understanding these laws is crucial as they directly influence how information is safeguarded and managed across various sectors.
Several significant laws have been enacted globally to address the complexities of data protection:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – Originating from the European Union, this law sets stringent standards for the collection, processing, and transfer of personal data. Its impact is felt worldwide due to its extraterritorial applicability.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) – Enforced in the United States, this act grants California residents enhanced rights over their personal information, including the right to know about the data collected, to request its deletion, and to opt out of its sale.
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) of Singapore – This legislation outlines the responsibilities of organizations in handling personal data, emphasizing consent, purpose, and reasonableness in data usage.
- Data Protection Act 2018 (UK) – Building on the GDPR, this act tailors data protection to the UK context, including provisions for law enforcement processing and national security.
The impact of these laws extends beyond mere compliance; they foster a culture of accountability among organizations and empower citizens with rights over their personal information. For instance, the GDPR’s requirement for explicit consent before data processing has led to more transparent practices and increased awareness among consumers about their data rights.
Moreover, these laws have prompted technological innovations aimed at enhancing data security and privacy. For example, the development of encryption technologies and anonymization techniques has been spurred by the need to comply with stringent data protection standards.
In conclusion, the legal landscape of data protection is dynamic and continually evolving to meet new challenges posed by technological advancements. These laws not only protect individual rights but also encourage a more responsible and transparent approach to data management across the globe.
Technological Tools for Enhancing Privacy

In this section, we delve into the various technological advancements that aid in the protection of personal information. These tools are crucial in today’s digital age, where data breaches and unauthorized access are prevalent. We will explore how these technologies can effectively shield sensitive data from potential threats.
To begin with, encryption stands out as a fundamental tool in safeguarding data. It transforms readable information into coded text that can only be deciphered with the correct decryption key. This method is widely used in secure communications and data storage to prevent unauthorized access.
Another powerful tool is the use of virtual private networks (VPNs). VPNs create a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, masking your IP address and encrypting your internet traffic. This not only protects your online activities from prying eyes but also allows you to access region-restricted content.
Moreover, privacy-focused browsers and extensions can significantly enhance your online security. These tools block trackers, prevent data collection, and sometimes even offer additional features like ad-blocking, which reduces the amount of data shared with third parties.
Lastly, password managers are essential in today’s digital landscape. They generate strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts and store them securely, ensuring that even if one account is compromised, others remain safe.
| Tool | Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Converts data into coded text | Prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information |
| VPNs | Encrypts internet traffic and hides IP address | Enhances online anonymity and security |
| Privacy Browsers/Extensions | Blocks trackers and reduces data sharing | Increases control over personal data online |
| Password Managers | Generates and stores secure passwords | Reduces risk of account breaches |
Educating the Public on Data Protection
In this section, we delve into the critical role of public education in enhancing awareness and understanding of data security practices. The aim is to foster a community that is well-informed and proactive in safeguarding their digital information.
The Importance of Education: As technology continues to evolve, so do the methods used by cybercriminals to exploit personal data. Educating the public is not just beneficial; it is essential. By providing clear, accessible information about data protection, individuals can make informed decisions about how they interact with digital platforms.
Key Topics for Public Education: Educational initiatives should cover a range of topics, including understanding the types of personal data that are collected, the risks associated with data breaches, and practical steps to secure personal information. This includes teaching about strong password management, recognizing phishing attempts, and the use of privacy settings on social media and other online services.
Strategies for Effective Education: To be effective, educational programs must be tailored to different age groups and technical proficiencies. Schools, community centers, and online platforms can all be leveraged to disseminate information. Interactive workshops, webinars, and online tutorials can make learning about data protection engaging and relevant.
Government and Community Partnerships: Governments play a pivotal role in coordinating and funding public education campaigns. Collaborating with community organizations, tech companies, and educational institutions can amplify the reach and impact of these initiatives. Such partnerships ensure that the message of data protection is consistent and reinforced across various channels.
In conclusion, educating the public on data protection is a multifaceted endeavor that requires ongoing commitment and innovation. By empowering individuals with knowledge, we can collectively build a safer digital environment.
Role of Government in Safeguarding Privacy
This section delves into the pivotal role that governmental bodies play in protecting the confidentiality of personal information. It explores how policies and regulations are crafted to ensure that the handling of sensitive data aligns with ethical standards and legal requirements.
Regulatory Frameworks: Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the need for robust frameworks to govern data management. These frameworks are designed to prevent misuse and unauthorized access, ensuring that data handlers adhere to strict protocols.
Enforcement of Privacy Laws: The effectiveness of privacy laws heavily depends on their enforcement. Government agencies are tasked with monitoring compliance and taking action against violations. This includes hefty fines and legal actions against entities that fail to protect personal data.
Promotion of Transparency: Governments encourage transparency in data practices by requiring companies to disclose how they collect, use, and share personal information. This transparency helps individuals understand and control how their data is being utilized.
Education and Awareness: Another critical role of government is to educate the public about data protection. By raising awareness about privacy rights and best practices, governments empower citizens to make informed decisions about their personal information.
International Cooperation: In the global digital landscape, governments collaborate to harmonize privacy standards. This international cooperation is essential for protecting data across borders and ensuring that privacy rights are upheld regardless of geographical location.
In conclusion, the government’s role in safeguarding privacy is multifaceted, involving regulation, enforcement, transparency, education, and international collaboration. Each of these elements is crucial for creating a secure environment where personal data is respected and protected.
Corporate Responsibility in Data Handling
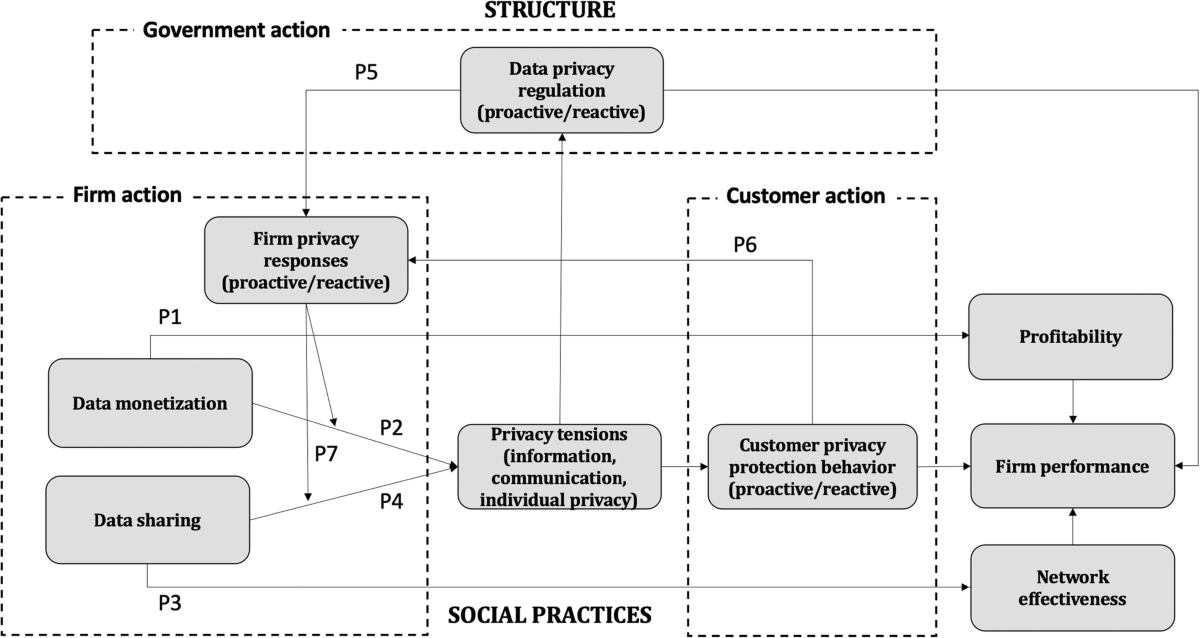
In this section, we delve into the critical role that corporations play in managing personal information. As entities that often collect, process, and store vast amounts of data, companies have a pivotal responsibility to ensure this information is handled with the utmost care and respect for individual rights.
Understanding Corporate Obligations: Corporations must navigate a complex landscape of legal requirements and ethical considerations when it comes to data handling. This involves not only complying with relevant legislation but also fostering a culture of transparency and accountability within the organization.
Legal Frameworks and Compliance: Companies are increasingly subject to stringent regulations that govern how they can use and protect personal data. Compliance with these laws is essential, medium.com as it not only protects the rights of individuals but also helps maintain the company’s reputation and trustworthiness.
Ethical Data Management: Beyond legal compliance, ethical considerations are paramount. This includes being transparent about data collection practices, ensuring data is used for legitimate purposes, and implementing robust security measures to prevent breaches.
Promoting Transparency: Corporations should clearly communicate their data handling practices to consumers. This transparency builds trust and allows individuals to make informed decisions about their data.
Security Measures: Implementing strong security protocols is a non-negotiable aspect of corporate responsibility in data handling. This includes encryption, secure data storage, and regular security audits to identify and mitigate risks.
Continuous Improvement: Companies must continually assess and improve their data handling practices. This involves staying abreast of technological advancements and adapting policies to reflect evolving best practices in data security and privacy.
In conclusion, the corporate sector plays a crucial role in safeguarding personal information. By adhering to both legal and ethical standards, companies can contribute significantly to a more secure and respectful digital environment.
The Psychology of Sharing Personal Information Online
This section delves into the intricate dynamics that govern the disclosure of personal details in the digital realm. It explores the motivations and fears that drive individuals to share or withhold information, providing a comprehensive understanding of the psychological underpinnings of online self-disclosure.
Understanding Motivations: People often share personal information online due to a variety of psychological drivers. These can include the desire for social connection, the pursuit of validation, or the need to express oneself freely. The digital environment, with its vast potential for connectivity, often amplifies these motivations.
Risks and Fears: Conversely, the fear of privacy breaches and the potential misuse of personal data can significantly influence an individual’s willingness to share information. This fear is not unfounded, given the prevalence of data leaks and the misuse of personal information by entities ranging from corporations to cybercriminals.
Impact of Social Norms: Social norms and peer behavior also play a crucial role in shaping online sharing habits. Observing others share personal details can normalize such behavior, making it more acceptable and expected within certain online communities.
Technological Influence: The design of social media platforms and other digital tools can subtly encourage or discourage the sharing of personal information. Features like easy sharing options, feedback mechanisms (likes, comments), and the visibility of others’ sharing behaviors can all influence an individual’s decision to disclose personal information.
In conclusion, the psychology of sharing personal information online is a complex interplay of individual desires, societal expectations, and technological influences. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing strategies that balance the benefits of digital connectivity with the need for personal data protection.
Global Perspectives on Privacy Rights
In this section, we delve into the diverse viewpoints regarding the protection of personal information across various regions. The discussion aims to highlight the complexities and nuances in the international approach to safeguarding individual data.
Legal Frameworks and Cultural Differences: Across the globe, the interpretation and enforcement of privacy rights vary significantly. For instance, European nations, under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), have stringent laws that emphasize the rights of the data subject. In contrast, some Asian countries might prioritize economic growth and technological advancement over strict privacy regulations.
Challenges in International Cooperation: One of the major hurdles in establishing a universal standard for privacy rights is the lack of a one-size-fits-all solution. Legal frameworks must consider not only the technological capabilities but also the cultural, social, and economic contexts of each region.
Emerging Economies and Privacy: In rapidly developing economies, the balance between fostering innovation and protecting privacy is delicate. These regions often face the challenge of implementing robust privacy measures without stifling technological progress.>
Global Trends and Future Directions: As the digital landscape continues to evolve, there is an increasing recognition of the need for global standards that respect local nuances. Initiatives like the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Privacy Framework and the Council of Europe’s Convention 108+ are steps towards harmonizing privacy protections across borders.
Understanding these global perspectives is crucial for developing effective policies that protect personal information while promoting global connectivity and innovation.
Future Trends in Cybersecurity and Privacy
As we navigate through the complexities of the digital era, the realm of cybersecurity and privacy continues to evolve at a rapid pace. This section delves into the emerging trajectories that are shaping the way we protect and manage sensitive information in the global context. It explores how different regions approach the delicate balance between technological advancement and the safeguarding of personal data.
The global landscape of privacy rights is marked by a diverse array of regulations and cultural attitudes. In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) stands as a pivotal framework, emphasizing stringent controls over data processing and robust rights for data subjects. Conversely, in the United States, privacy laws are more sector-specific, with a patchwork of regulations that vary by industry and state. Asia, with its vast economic and technological growth, presents a mix of approaches, from the comprehensive Personal Data Protection Act in Singapore to the evolving legal frameworks in China.
These regional differences highlight the need for a nuanced understanding of privacy rights. As technology becomes increasingly integrated into daily life, the challenge lies in harmonizing these disparate approaches to ensure a consistent level of protection for all users, regardless of their location. This involves not only legal harmonization but also a deeper cultural shift towards recognizing the value of personal data and the importance of its protection.
Moreover, the rise of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and blockchain is redefining the privacy landscape. These technologies offer both opportunities for enhanced security measures and new avenues for potential breaches. The future of cybersecurity and privacy will likely see a greater emphasis on adaptive security architectures that can evolve with these technologies, as well as international collaborations to tackle cross-border data issues.
In conclusion, the global perspective on privacy rights is a dynamic and multifaceted issue. As we look to the future, it is imperative to foster a global dialogue that respects cultural and legal diversity while striving for a unified front against the ever-evolving threats to personal data security. This will require innovative solutions, robust legal frameworks, and a collective commitment to protecting the fundamental right to privacy in the digital age.
Empowering the Individual: Practical Steps for Privacy

In this section, we delve into the multifaceted global perspectives that shape the understanding and implementation of privacy rights. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the approach to personal data protection varies significantly across different regions and cultures. This diversity in viewpoint and regulation provides a rich backdrop against which we can explore the practical steps individuals can take to safeguard their personal information.
Different countries have adopted unique frameworks to address the challenges of digital surveillance and data protection. For instance, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets a high standard for privacy and data protection. It mandates that companies must explicitly ask for consent before collecting personal data and must provide clear explanations about how this data will be used. This regulation has influenced many other regions to reconsider their own privacy laws, leading to a more robust global conversation about the rights of individuals in the digital age.
Conversely, in the United States, privacy laws are more fragmented, with different rules applying to different sectors. This patchwork approach can sometimes lead to confusion and gaps in protection. However, it also allows for flexibility and innovation in how companies handle personal data, which can be beneficial in a rapidly changing technological environment.
In Asia, countries like China and India have their own distinct approaches to privacy. China, with its extensive surveillance infrastructure, has stringent data protection laws that align with its national security interests. India, on the other hand, is in the process of implementing comprehensive data protection legislation that seeks to balance the needs of businesses with the rights of individuals.
Understanding these global perspectives is crucial for individuals seeking to protect their personal information. By being aware of the legal frameworks in place in different regions, individuals can make informed decisions about where to store their data and which services to use. Moreover, knowledge of global trends can empower individuals to advocate for stronger privacy protections in their own communities.
In conclusion, the global landscape of privacy rights is complex and varied. Each region brings its own set of challenges and solutions to the table. By exploring these diverse perspectives, individuals can better equip themselves with the knowledge and tools necessary to protect their personal data in an increasingly interconnected world.
